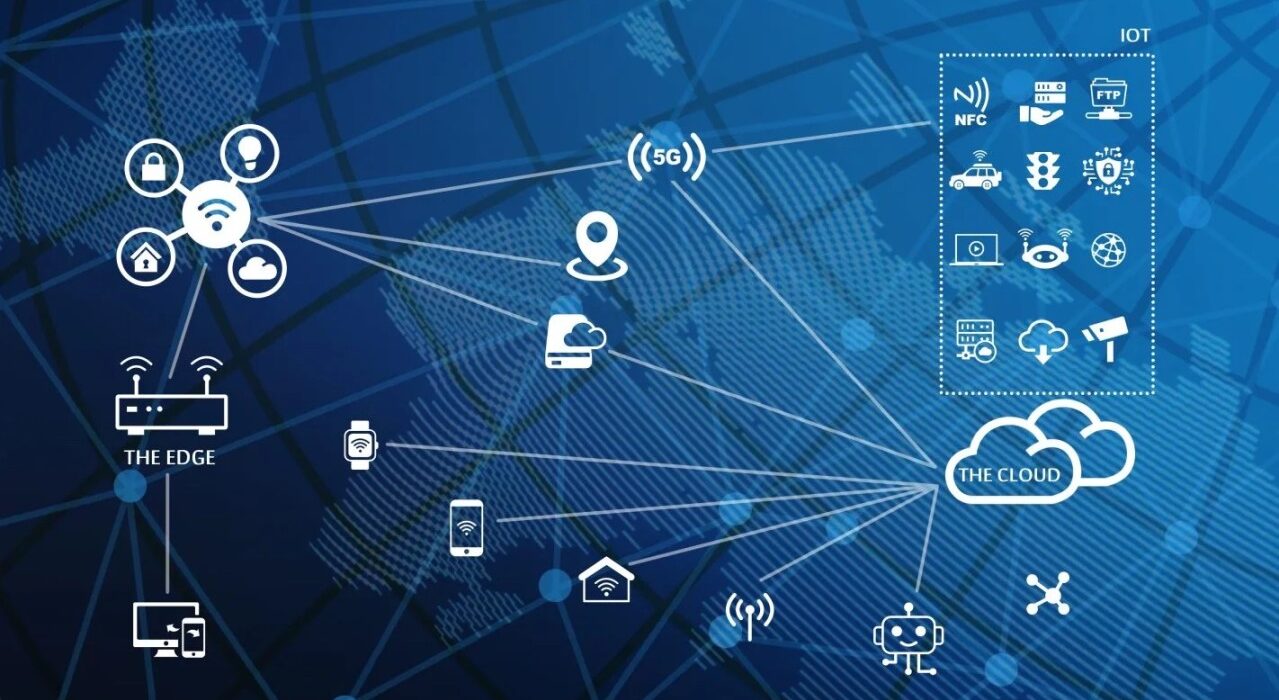
Introduction
As the demand for low-latency processing and real-time analytics grows, edge computing has emerged as a transformative technology. By processing data closer to the source—at the “edge” of the network—this approach minimizes latency, reduces bandwidth usage, and enhances the efficiency of IoT, AI, and cloud applications. Innovations in edge computing are reshaping industries, enabling smarter devices, and optimizing cloud interactions.
Key Innovations in Edge Computing
1. AI-Powered Edge Devices
- AI and machine learning models are increasingly being embedded directly into edge devices.
- Neural Processing Units (NPUs) and AI accelerators allow devices to perform real-time decision-making without relying on cloud resources.
- Examples: Smart cameras with facial recognition, predictive maintenance in manufacturing, and autonomous vehicles.
2. 5G and Edge Synergy
- The rollout of 5G networks has significantly enhanced edge computing capabilities by providing ultra-low latency and high-speed data transmission.
- Applications include immersive AR/VR experiences, autonomous drones, and real-time remote healthcare monitoring.
3. Federated Learning at the Edge
- Instead of sending raw data to a central cloud, federated learning enables edge devices to train AI models locally while only sharing aggregated insights.
- This enhances data privacy and security, particularly in industries like healthcare and finance.
4. Micro Data Centers and Edge Nodes
- Traditional cloud infrastructure is complemented by edge micro data centers, which process and store data closer to users.
- These compact, scalable units enable businesses to deploy high-performance computing resources at the edge without needing large-scale cloud data centers.
5. Serverless and Containerized Edge Computing
- Containers (Docker, Kubernetes) and serverless computing (AWS Lambda, Azure Functions) are extending to edge environments.
- This enhances flexibility and scalability while reducing resource consumption.
Applications of Edge Computing
- Autonomous Vehicles: Enables real-time decision-making for navigation and obstacle avoidance.
- Smart Cities: Optimizes traffic management, security surveillance, and energy consumption.
- Healthcare: Facilitates real-time patient monitoring and diagnostics without relying on cloud processing.
- Retail & Manufacturing: Enhances inventory tracking, quality control, and supply chain automation.
Challenges and Considerations
- Security Risks: More distributed endpoints mean increased attack surfaces for cyber threats.
- Interoperability Issues: Integrating various edge devices with cloud and legacy systems requires standardization.
- Cost and Infrastructure: Deploying and maintaining edge nodes can be costly, requiring strategic investment.
Future Trends in Edge Computing
- Edge-AI Co-evolution: More sophisticated AI models will be optimized for edge processing.
- Blockchain at the Edge: Secure, decentralized transactions for IoT and edge devices.
- Energy-Efficient Edge Computing: Sustainability-driven innovations, including green energy-powered edge nodes.